Nearsightedness vs Farsightedness: Your Complete Guide to Common Vision Problems
The quick answer: Nearsightedness (myopia) means you see close objects clearly, but distant objects appear blurry. Farsightedness (hyperopia) means you see distant objects clearly, but close-up objects are blurry. Both are types of refractive error that affect how light rays focus in your eyes, and both are easily treatable with the right vision correction.
Understanding the difference between these conditions helps you recognize symptoms and seek proper treatment from an eye doctor. Let’s explore everything you need to know about these vision problems.
Nearsightedness (Myopia): Everything You Need to Know
What Is Nearsightedness?
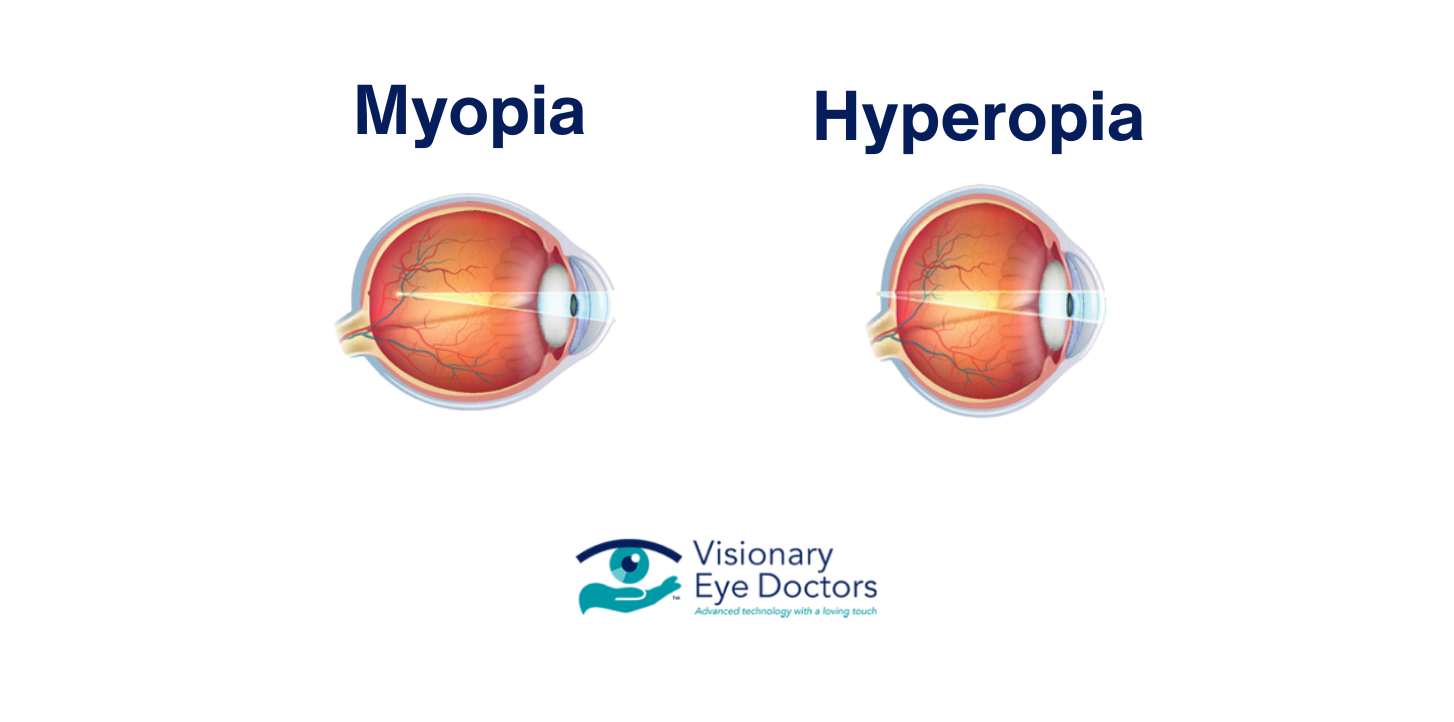
Nearsightedness, or myopia, is a common refractive error where nearby objects appear clear, but distant objects look blurry. This happens because your eye’s shape causes light rays to focus in front of the retina instead of directly on it. The retina is a light-sensitive tissue at the back of your eye that sends electrical impulses through the optic nerve to your brain.
What Causes Myopia?
Nearsightedness occurs when your eyeball is too long or your cornea (the clear front surface of your eye) is too curved. This changes where the focal point lands in your eye. Instead of light focusing directly on the retina for normal vision, it focuses in front of it, creating blurry vision when looking at distant objects.
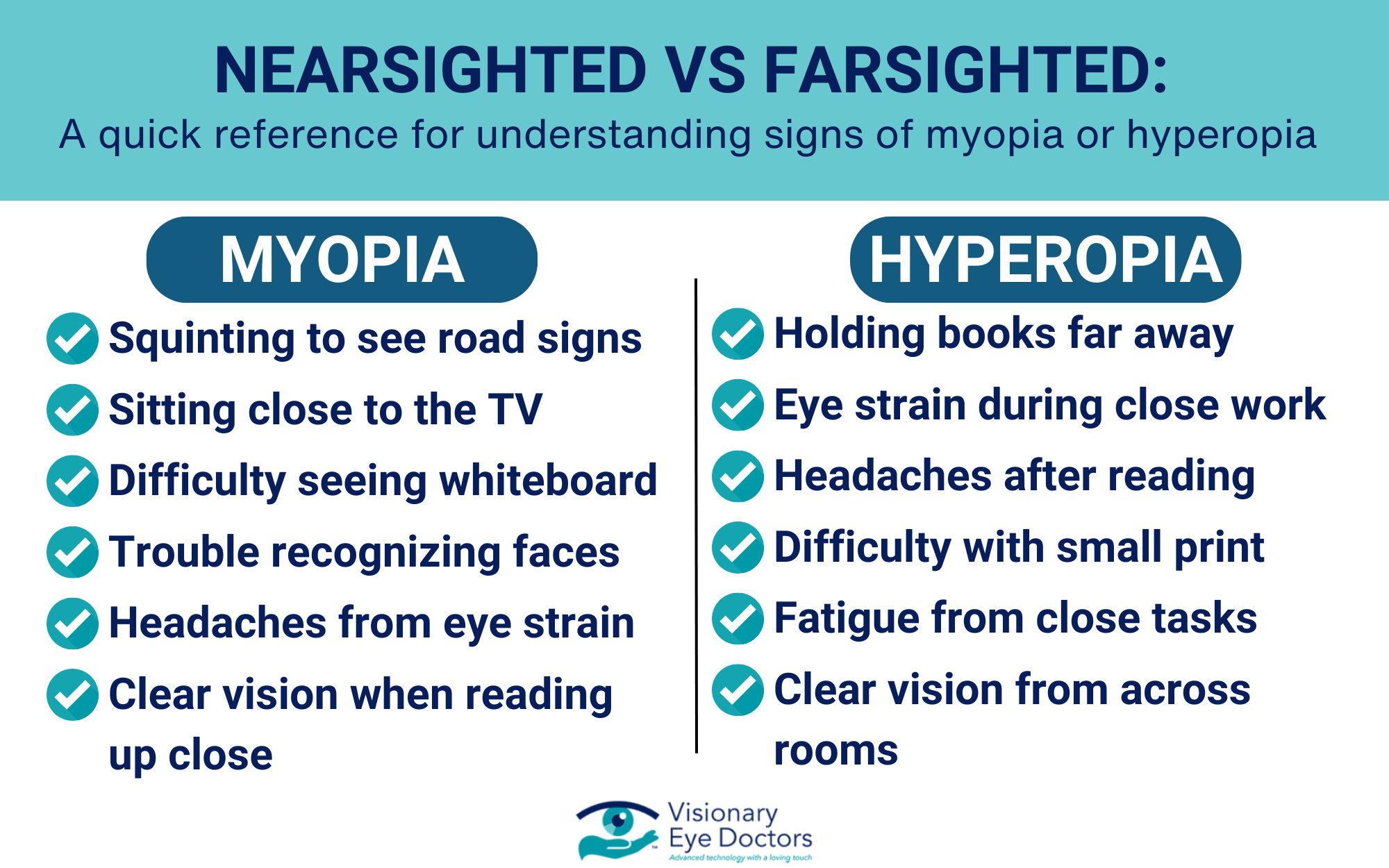
Common Signs of Nearsightedness:
- Squinting to see distant objects clearly
- Difficulty reading road signs while driving
- Sitting close to the TV or movie screen
- Holding books or devices close to your face
- Eye strain and headaches from trying to focus
- Difficulty seeing the board at school or work
How Myopia Affects Daily Activities
Nearsighted individuals often struggle with activities that require distance vision:
- Driving: Difficult, especially at night when road signs are harder to see
- Playing Sports: Difficult when you can’t clearly see the ball or other players across the field
- Entertainment: Watching movies in theaters becomes frustrating without proper vision correction
- Social Situations: Recognizing faces across a room can be challenging
Treatment Options for Nearsightedness
Several effective treatments can restore clear vision for people with myopia:
- Prescription Glasses: The most common solution, glasses with the correct prescription provide immediate, clearer vision for distant objects.
- Contact Lenses: Contacts offer freedom from glasses and a wider field of vision. Daily, weekly, and monthly options are available.
- Refractive Surgery: LASIK (laser in situ keratomileusis) and other laser procedures can permanently correct myopia by reshaping the cornea.
- Orthokeratology (Ortho-K): Special contact lenses worn overnight temporarily reshape the cornea, providing clear vision during the day without glasses or contacts. Visionary Eye Doctors offers Ortho-K treatment for qualified patients.
When Does Myopia Develop?
Nearsightedness often starts in childhood and may worsen during the teenage years as the eyes continue growing. Environmental factors like increased screen time and less outdoor activity may contribute to its development. Regular eye exams are essential for monitoring a child’s vision and catching changes early.
Farsightedness (Hyperopia): Everything You Need to Know
What Is Farsightedness?
Farsightedness, or hyperopia, is a refractive error where distant objects appear clearer than close-up objects. Unlike myopia, hyperopia causes light rays to focus behind the retina instead of directly on it. This makes close-up vision more challenging than distance vision.
What Causes Hyperopia?
Farsightedness happens when your eyeball is too short or your cornea is too flat. This changes how light enters your eye and where it focuses. The focal point lies behind the retina, making nearby objects appear blurry while distant objects may remain relatively clear.
Common Signs of Farsightedness:
- Difficulty reading books, newspapers, or phone screens
- Eye strain during close work
- Headaches after reading or computer work
- Blurry vision when looking at close-up objects
- Fatigue after activities requiring near vision
- Children may have trouble with schoolwork or reading
How Hyperopia Affects Daily Activities
Farsighted vision significantly impacts activities requiring close-up vision:
- Reading: Becomes uncomfortable and tiring without proper correction
- Computer Work and Smartphones: Often cause eye strain and headaches during extended use
- Hobbies: Crafts, sewing, or detailed work become difficult to perform
- Daily Tasks: Simple activities like checking price tags while shopping can be challenging without proper corrective lenses
Treatment Options for Farsightedness
Multiple treatment options can help people with hyperopia achieve clear vision:
- Reading Glasses: Over-the-counter or prescription reading glasses help with close-up tasks.
- Bifocals and Progressive Lenses: These prescription glasses correct both distance and near vision in one lens.
- Contact Lenses: Multifocal contacts or single-vision contacts can correct farsighted vision.
- Refractive Surgery: Laser procedures can reshape the cornea to improve the eye’s ability to focus light properly on the retina.
When Does Hyperopia Develop?
Many people are born with mild farsightedness that may not cause problems until later in life. As we age, the eye’s natural lens becomes less flexible, making it harder to focus on close objects. This is why farsightedness often becomes noticeable in early adulthood or middle age, even if it was present from birth.
How Eye Doctors Diagnose Vision Problems
Getting an accurate diagnosis is the first step toward a clear vision. During a regular eye exam, your eye doctor will perform several tests to determine if you have a refractive error and what type of vision correction you need.
- Visual Acuity Test: You’ll read letters on an eye chart to measure how well you see at various distances. This helps determine your level of visual acuity.
- Refraction Test: Your eye doctor will use a device called a phoropter to test different prescription lenses. You’ll look through various lenses and tell the doctor which ones make your vision clearer.
- Eye Health Examination: Beyond checking your vision, the eye doctor will examine the overall health of your eyes, including the retina and optic nerve.
The American Optometric Association recommends regular eye exams even if you don’t notice vision problems. Many refractive errors develop gradually, and early detection leads to better treatment outcomes.
Why Professional Diagnosis Matters
Online vision tests and self-diagnosis can’t replace a proper eye exam. Only a qualified eye doctor can determine the exact type and degree of your refractive error, rule out other eye health issues, and prescribe the correct treatment. They can also detect other vision problems that might be affecting your sight.
General Eye Health Tips
Taking care of your eyes goes beyond correcting refractive errors. These simple habits can help maintain good eye health and reduce eye strain:
- Follow the 20-20-20 Rule: Every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds. This helps reduce eye strain from close work and screen time.
- Ensure Proper Lighting: Use adequate lighting when reading or doing close work. Avoid working in low light, making your eyes work harder.
- Schedule Regular Eye Exams: Most adults should have an eye exam every 1-2 years, or as recommended by their eye doctor. Children should have their first eye exam by age 3, with regular checkups as they grow.
- Protect Your Eyes from UV Damage: Wear sunglasses that block 100% of UV rays when outdoors. Long-term UV exposure can contribute to various eye problems.
Contact your eye doctor if you experience sudden vision changes, severe eye pain, flashing lights, or other urgent symptoms.
Your Path to Clearer Vision
Both nearsightedness and farsightedness are very common and highly treatable vision problems. The key is getting an accurate diagnosis and finding the right treatment option for your lifestyle and needs.
Whether you’re struggling to see distant objects clearly or finding it hard to read up close, don’t let a vision problem limit your daily activities. Modern treatment options, from traditional prescription glasses to advanced refractive surgery, can help you achieve the clear vision you deserve.
Schedule an eye exam with the qualified eye doctors at Visionary Eye Doctors to determine which type of refractive error you have and explore your treatment options. With the right vision correction, you can get back to enjoying all the activities that matter most to you.