Early Signs of Glaucoma: What You Need to Know to Protect Your Vision
The short answer: The most common type of glaucoma, open-angle glaucoma, typically has no early warning signs or noticeable symptoms. This is why glaucoma is often called the “silent thief of sight.” However, acute angle-closure glaucoma can cause sudden, severe symptoms requiring immediate medical attention. Regular comprehensive eye exams are the only reliable way to detect glaucoma before permanent vision loss occurs.
What Is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that cause progressive damage to the optic nerve, the vital connection that sends visual information from your eyes to your brain. In most cases, this damage is associated with elevated intraocular pressure (the pressure inside your eye).
Your eye constantly produces a clear fluid called aqueous humor. This fluid nourishes the eye and maintains its shape. It normally drains through the trabecular meshwork at the drainage angle where the iris meets the cornea. When this drainage system doesn’t work properly, fluid builds up and increases pressure, potentially damaging the optic nerve over time.
If left untreated, glaucoma can lead to permanent vision loss, making it the second leading cause of blindness worldwide. However, with early detection and proper treatment, most people can preserve their vision for years to come.
Types of Glaucoma
Open-Angle Glaucoma
Primary open-angle glaucoma is the most common form, accounting for about 90% of cases. The drainage angle remains open, but the trabecular meshwork becomes less efficient over time, causing a gradual increase in eye pressure.
This type develops so slowly that most people don’t notice changes until significant optic nerve damage has occurred. Vision loss typically begins with peripheral vision, which many people don’t immediately recognize. Because the changes happen gradually, your brain often compensates, making it even harder to detect without a professional exam.
Angle-Closure Glaucoma
Acute angle-closure glaucoma occurs when the iris bulges forward and completely blocks the drainage angle, causing a rapid spike in eye pressure. This is a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to prevent permanent damage.
Chronic angle-closure glaucoma develops more gradually as the iris slowly blocks the drainage angle over time. Some people may experience intermittent episodes where the angle temporarily closes, causing brief symptoms that resolve on their own before a full acute attack occurs.
Normal-Tension Glaucoma
Some people develop optic nerve damage even with normal eye pressure. Researchers believe factors such as reduced blood flow to the optic nerve may play a role. This highlights why comprehensive eye exams evaluating optic nerve health are essential, not just pressure checks.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Glaucoma

Open-Angle Glaucoma: The Silent Threat
The most challenging aspect of open-angle glaucoma is that there are typically no obvious symptoms in the early stages. Up to half of the people with glaucoma don’t know they have it until the disease has progressed significantly.
As the disease progresses, you may notice:
- Patchy blind spots in your peripheral vision
- Difficulty seeing objects to your side while looking straight ahead
- In advanced stages, tunnel vision occurs, where only central vision remains
Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma: A Medical Emergency
Unlike open-angle glaucoma, acute angle-closure produces sudden, severe symptoms:
- Severe eye pain and intense headache
- Sudden blurry or decreased vision
- Halos or rainbow-colored rings around lights
- Eye redness, nausea, and vomiting
Subtle Warning Signs to Watch For
Some people may experience intermittent warning signs before a full acute attack or in the early stages of certain types of glaucoma. These can include occasional blurry vision, mild headaches or eye discomfort, seeing halos around lights at night, and needing more light to see clearly. If you notice any of these symptoms, schedule an appointment with your eye doctor for evaluation.
Who Is at Higher Risk?
While anyone can develop glaucoma, certain factors increase your risk:
- Age: Risk increases significantly after 60. For African Americans, elevated risk begins around age 40.
- Family history: Having an immediate family member with glaucoma increases your risk four to nine times.
- Race and ethnicity: African Americans are six to eight times more likely to develop glaucoma. Hispanic Americans have an elevated risk after 60, and people of Asian descent have a higher risk for angle-closure glaucoma.
- Medical conditions: Diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease can increase risk.
- Eye factors: Previous eye injuries, severe nearsightedness, thin corneas, and elevated eye pressure.
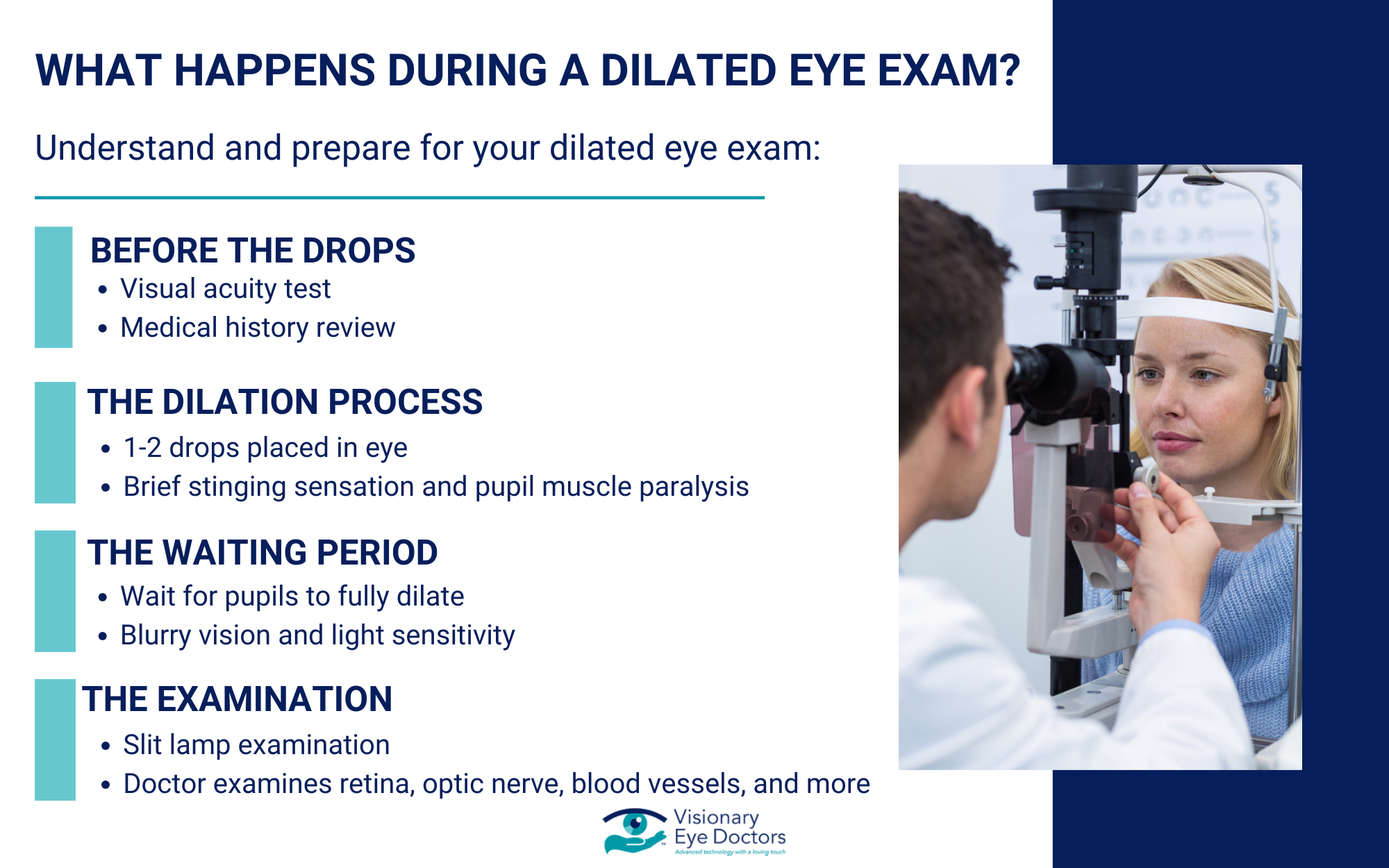
How Eye Doctors Detect Glaucoma
A comprehensive eye exam includes several tests to evaluate your glaucoma risk and detect early signs of the disease. Since vision loss from glaucoma is permanent and cannot be reversed, these exams are critical for catching the condition before damage occurs.
- Tonometry: Measures the pressure inside your eye
- Ophthalmoscopy: Examines the shape and color of your optic nerve for signs of damage
- Visual field testing: Maps your complete field of vision to detect blind spots you might not notice
- Gonioscopy: Examines the drainage angle to determine your glaucoma type or risk
- Pachymetry: Measures corneal thickness, which can affect the accuracy of pressure readings
These tests are painless and can identify problems before you experience any vision changes.
Glaucoma Treatment Options
While there’s no cure for glaucoma, effective treatments can control the disease and prevent further vision loss. The goal of treatment is to lower eye pressure to a level that prevents additional optic nerve damage.
Prescription eye drops are often the first line of treatment, working to reduce eye pressure by either decreasing fluid production or improving drainage. Laser treatment can improve fluid drainage: selective laser trabeculoplasty for open-angle glaucoma, or laser peripheral iridotomy for angle-closure glaucoma. Surgery may be recommended when other treatments aren’t sufficient, creating new drainage pathways to lower eye pressure.
Why Early Detection Matters
Vision loss from glaucoma is permanent and cannot be reversed, even with treatment. However, early detection and treatment can stop or significantly slow the progression of the disease, preserving your remaining vision for years or even decades.
The American Academy of Ophthalmology recommends that adults have a comprehensive eye exam around age 40, when early signs of eye disease often begin. If you have risk factors such as family history, elevated eye pressure, or certain health conditions, your eye doctor may recommend more frequent exams to monitor for changes.
Steps to Protect Your Eye Health

You can’t prevent glaucoma, but you can take proactive steps to catch it early and protect your sight.
- Schedule regular eye exams starting at age 40, with more frequent visits if you have risk factors.
- Know your family history and share it with your eye doctor.
- Manage your overall health by controlling diabetes and blood pressure, which supports good eye health.
- Protect your eyes from injury by wearing protective eyewear during sports and activities.
- Follow your treatment plan consistently if you’ve been diagnosed with glaucoma, even if you feel fine.
Schedule Your Eye Exam at Visionary Eye Doctors
Glaucoma may be the “silent thief of sight,” but it doesn’t have to steal your vision. Early detection through regular comprehensive eye exams is your best defense against this sight-threatening condition.
If you have risk factors for glaucoma or haven’t had an eye exam recently, don’t wait. Schedule a comprehensive eye exam with the experienced team at Visionary Eye Doctors. Our advanced diagnostic technology allows us to detect glaucoma in its earliest stages, giving you the best chance to preserve your vision.
With early detection and proper treatment, most people with glaucoma can maintain their sight and continue enjoying the activities that matter most. Taking that first step to schedule an exam could be the most important thing you do for your long-term eye health.