What is a Dilated Eye Exam? Your Complete Guide to Understanding This Important Procedure
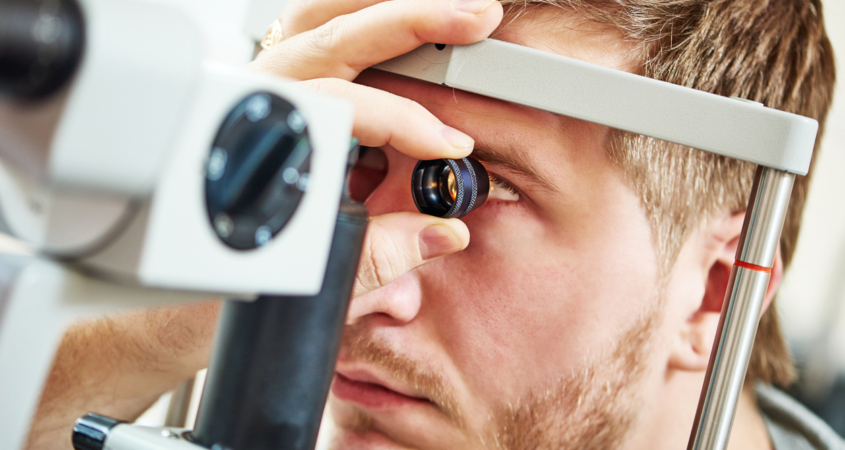
A dilated eye exam is a procedure where your eye doctor uses special drops to widen your pupils, allowing them to see inside your eye more clearly. This examination provides a comprehensive view of your retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels that isn’t possible during a routine eye exam.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about dilated eye exams:
- What happens during the procedure
- What conditions can be detected
- How to prepare for your appointment
- What to expect afterward
- Why these exams are crucial for maintaining your eye health and preventing vision loss
What is a Dilated Eye Exam?
A dilated eye exam is a more comprehensive type of eye exam where your eye doctor uses special eye drops to make your pupils larger. During a routine eye exam, your pupils are natural, which limits how much of the inside of your eye your doctor can see. When your pupils are dilated, they become much wider, giving your eye doctor a clear view of the entire retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels at the back of your eye. This view is crucial for detecting many eye diseases and health conditions that might not show noticeable symptoms in their early stages.
The dilation process involves placing special eye drops in your eyes that temporarily relax the muscles controlling your pupil size. These drops cause pupil dilation within 15-30 minutes, and the effects typically last 4-6 hours.
What Happens During Your Dilated Eye Exam?
Understanding what to expect can help ease any anxiety about your first dilated exam. Here’s the step-by-step process:
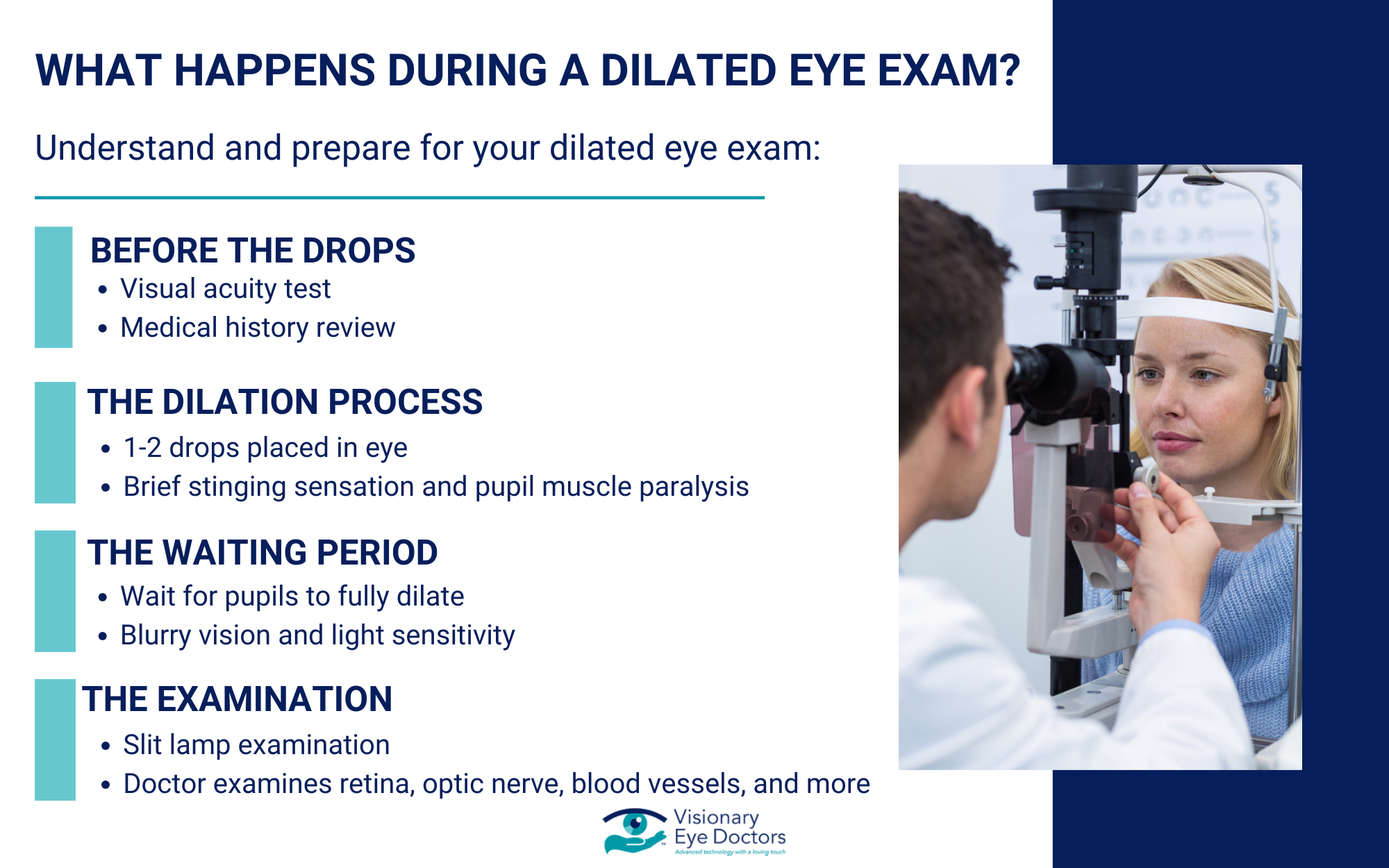
Step 1: Before the Drops
Your eye doctor will start with a standard visual acuity test and may perform other routine tests. They’ll also ask about your medical history, any vision problems you’ve noticed, and whether you have a family member with eye disease.
Step 2: The Dilation Process
Your doctor will place one or two drops of dilating medication in each eye. You might feel a slight sting for a few seconds, but this is normal and the exam itself is painless. The drops work by temporarily paralyzing the muscles that control your pupil size.
Step 3: The Waiting Period
After receiving the eye drops, you’ll wait 15-30 minutes for your pupils to fully dilate. During this time, you might start noticing some blurry vision and light sensitivity. This is completely normal and temporary.
Step 4: The Examination
Once your pupils are fully dilated, your eye doctor will use special instruments, including a slit lamp, to examine the inside of your eyes. They’ll look at your retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels to check for any signs of eye disease or other health conditions.
The entire process usually takes about an hour, including the waiting time for dilation.
What Can Your Eye Doctor See During a Dilated Exam?
A comprehensive dilated eye exam allows your eye doctor to detect potential issues that might not be visible during a routine eye exam. Here’s what they’re looking for:
- Diabetic Retinopathy: If you have diabetes, regular dilated exams are crucial for early detection of diabetic retinopathy. This condition damages the blood vessels in your retina and is a leading cause of vision loss in adults. Early detection means early treatment, which can prevent serious vision problems.
- Macular Degeneration: This eye condition affects the central part of your retina called the macula. Macular degeneration can cause significant vision loss, but when caught early through dilated exams, treatments can slow its progression.
- Glaucoma Detection: Your eye doctor can examine your optic nerve for signs of glaucoma, a serious eye disease that can lead to permanent vision loss if left untreated. Glaucoma often has no early warning signs, making dilated exams essential for detection.
- Other Eye Diseases: Dilated exams can also detect retinal tears, eye tumors, and signs of high blood pressure or other health conditions that affect your eyes.
After Your Dilated Eye Exam: What to Expect
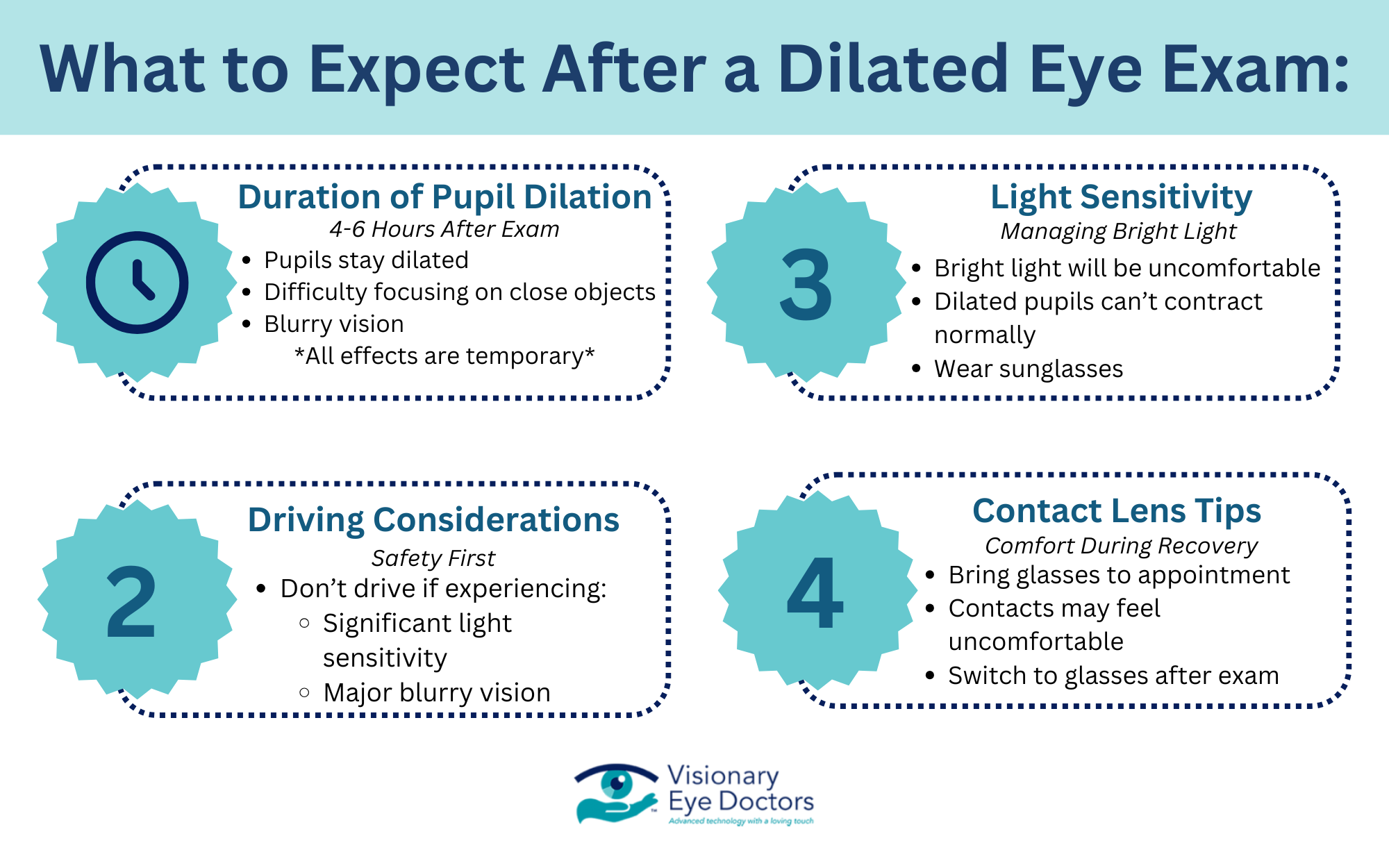
The side effects of eye dilation are temporary but important to understand:
- Duration and Effects: Your pupils will remain dilated for 4-6 hours after the exam. During this time, you’ll experience increased light sensitivity and may have difficulty focusing on close objects. Some people also notice blurry vision, especially when reading.
- Light Sensitivity: Bright light will be uncomfortable during the dilation period. The pupils normally contract to protect your eyes from too much light, but dilated pupils can’t perform this function. Wearing sunglasses, even indoors, can help manage this discomfort.
- Driving Considerations: Many people can drive after a dilated exam, but this varies from person to person. If you’re sensitive to bright light or experiencing significant blurry vision, it’s safer to arrange for someone to drive you home.
- Contact Lenses: If you wear contact lenses, you may want to bring glasses to your appointment. Some people find contacts uncomfortable while their eyes are dilated.
Who Needs Dilated Eye Exams and How Often?
Everyone should have regular eye exams, but certain factors put you at higher risk for eye disease. Many eye diseases have no noticeable symptoms in their early stages, making dilated exams often the only way to detect these conditions when they’re most treatable.
For most adults, annual dilated exams are recommended. However, you may need more frequent exams if you have certain risk factors:
- Adults over 40 should have dilated exams annually
- People with diabetes need dilated exams at least once a year
- Those with a family history of eye disease may need more frequent exams
- Individuals with high blood pressure should have regular dilated exams
Even if you only think you need glasses for a refractive error like nearsightedness, a dilated exam can detect other eye problems you might not know about. If you have multiple risk factors like diabetes or a family history of eye disease, your eye doctor might recommend more frequent exams than the standard annual schedule.
Take Control of Your Eye Health
A dilated eye exam is one of the most important tools for protecting your vision and overall eye health. While the temporary side effects might seem inconvenient, the early detection of serious eye conditions can prevent permanent vision loss and help maintain your quality of life.
Many eye diseases develop slowly without causing noticeable symptoms until significant damage has occurred. Regular dilated exams give you and your eye doctor the best chance to catch potential issues early when treatment is most effective.
At Visionary Eye Doctors, we understand that comprehensive eye care goes beyond just checking if you need glasses. Our dilated eye exams use the latest technology to provide thorough evaluations of your eye health. We take the time to explain what we’re looking for and what your results mean for your vision.
Don’t wait until you notice vision problems to schedule your next comprehensive dilated eye exam. Early detection is your best defense against vision loss. Contact Visionary Eye Doctors today to schedule your appointment and take a proactive step toward protecting your precious eyesight.